ASTM D2152-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone Immersion
Standard Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone Immersion
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This test method is applicable only for distinguishing between inadequately fused and adequately fused PVC. The difference between thermally degraded and adequately fused PVC cannot be detected by this test method. Acetone immersion is not a substitute for burst, impact, or other physical or chemical tests on PVC pipe or fittings and it, therefore, shall not be used as the only test specification for purchasing of PVC pipe and fittings. This test only detects inadequate fusion and does not determine the over-all quality of the PVC pipe or fittings.
3.2 This test method is useful in determining whether inadequate fusion contributed to failure of PVC pipe or fittings in other physical or chemical tests, or in service.
3.3 This test method is useful in evaluating the adequacy of PVC fusion obtained in process or materials trials.
3.4 This test method determines adequacy of fusion on a single, relatively small specimen. This test method requires the use of a hazardous reagent which must be properly handled and disposed. Therefore, this test method may not be cost-effective to employ as a routine quality control test.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the adequacy of fusion of extruded rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) pipe and molded fittings as indicated by reaction to immersion in anhydrous acetone.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard except where instruments are calibrated in SI units.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Specific hazards statements are given in Annex A1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2152 − 17 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
1
Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone Immersion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2152; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* notbeusedastheonlytestspecificationforpurchasingofPVC
pipe and fittings. This test only detects inadequate fusion and
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the ad-
does not determine the over-all quality of the PVC pipe or
equacy of fusion of extruded rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)
fittings.
pipe and molded fittings as indicated by reaction to immersion
in anhydrous acetone. 3.2 This test method is useful in determining whether
inadequatefusioncontributedtofailureofPVCpipeorfittings
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
in other physical or chemical tests, or in service.
as the standard except where instruments are calibrated in SI
units. 3.3 This test method is useful in evaluating the adequacy of
PVC fusion obtained in process or materials trials.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.4 This test method determines adequacy of fusion on a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
single,relativelysmallspecimen.Thistestmethodrequiresthe
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
useofahazardousreagentwhichmustbeproperlyhandledand
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to us-
disposed.Therefore, this test method may not be cost-effective
e.Specific hazards statements are given in Annex A1.
to employ as a routine quality control test.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4. Apparatus
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 Container—Either individual, sealable containers for
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
each specimen or one large, airtight container capable of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
holding several specimens without touching one another.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.2 Hydrometer and Cylinder—Precision hydrometer,
graduated in thousandths, with a minimum range of 0.780 to
2. Referenced Documents
0.790 g/mL and a cylinder large enough to immerse the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
hydrometer.
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
4.3 Thermometer—ASTM 12C total immersion
3. Significance and Use thermometer,rangefrom−20°Cto102°Caccurateto0.2°C,or
equivalent.
3.1 This test method is applicable only for distinguishing
between inadequately fused and adequately fused PVC. The
5. Reagent
difference between thermally degraded and adequately fused
5.1 Acetone—American Chemical Society Reagent Grade,
PVC cannot be detected by this test method. Acetone immer-
having a maximum density of 0.7857 g/mL at 25°C.
sion is not a substitute for burst, impact, or other physical or
chemical tests on PVC pipe or fittings and it, therefore, shall
NOTE1—SeeAnnexA1forthesafetyandhealthprecautionstobeused
with acetone.
5.2 Prior to conducting the test, check the density of the
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
acetone with a precision hydrometer to determine its dryness.
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl
Based Pipe.
Ifthedensityoftheacetoneisgreaterthan0.934g/mLat23°C,
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2017. Published January 2018. Originally
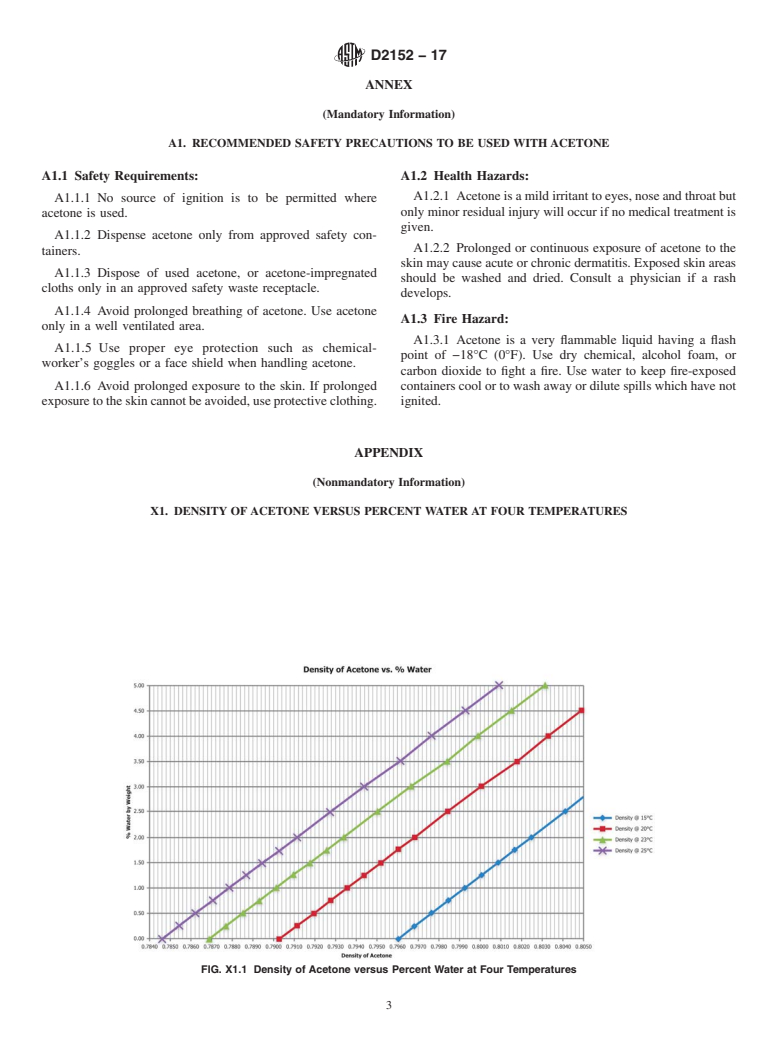
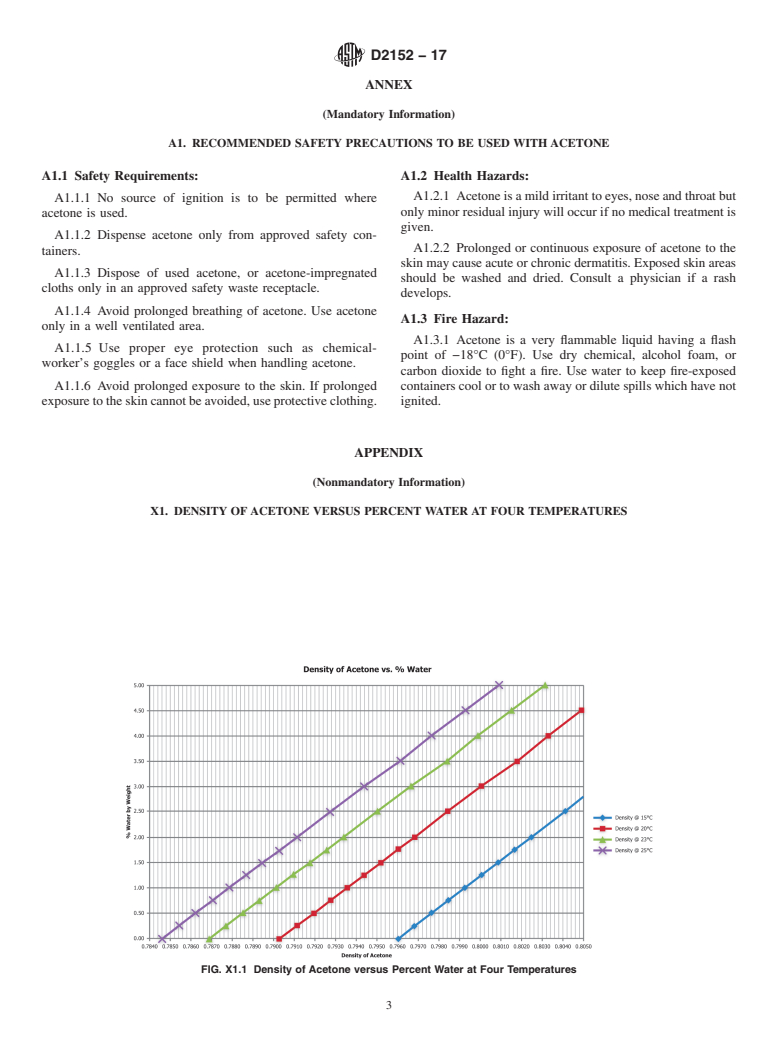
(corresponding to approximately 2% water by mass (see Fig.
approved in 1963T. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D2152–13. DOI:
X1.1)), use fresh acetone or dry the wet acetone with a drying
10.1520/D2152-17.
2
agent. Recheck the density of the fresh or dried acetone before
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
using.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. NOTE 2—Wet acetone can be dried by thoroughly agitating it with at
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -----------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2152 − 13 D2152 − 17 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
1
Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone Immersion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2152; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the adequacy of fusion of extruded rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) pipe and
molded fittings as indicated by reaction to immersion in anhydrous acetone.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard except where instruments are calibrated in SI units.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Specific hazards statements are given in Annex A1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
3. Significance and Use
3.1 This test method is applicable only for distinguishing between inadequately fused and adequately fused PVC. The difference
between thermally degraded and adequately fused PVC cannot be detected by this test method. Acetone immersion is not a
substitute for burst, impact, or other physical or chemical tests on PVC pipe or fittings and it, therefore, shall not be used as the
only test specification for purchasing of PVC pipe and fittings. This test only detects inadequate fusion and does not determine the
over-all quality of the PVC pipe or fittings.
3.2 This test method is useful in determining whether inadequate fusion contributed to failure of PVC pipe or fittings in other
physical or chemical tests, or in service.
3.3 This test method is useful in evaluating the adequacy of PVC fusion obtained in process or materials trials.
3.4 This test method determines adequacy of fusion on a single, relatively small specimen. This test method requires the use
of a hazardous reagent which must be properly handled and disposed. Therefore, this test method may not be cost-effective to
employ as a routine quality control test.
4. Apparatus
4.1 Container—Either individual, sealable containers for each specimen or one large, airtight container capable of holding
several specimens without touching one another.
4.2 Hydrometer and Cylinder—Precision hydrometer, graduated in thousandths, with a minimum range of 0.780 to 0.790 g/mL
and a cylinder large enough to immerse the hydrometer.
4.3 Thermometer—ASTM 12C total immersion thermometer, range from −20°C to 102°C accurate to 0.2°C, or equivalent.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl Based
Pipe.
Current edition approved May 1, 2013Nov. 1, 2017. Published June 2013January 2018. Originally approved in 1963T. Last previous edition approved in 20102013 as
D2152 – 95D2152 – 13.(2010). DOI: 10.1520/D2152-13.10.1520/D2152-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2152 − 17
5. Reagent
5.1 Acetone—American Chemical Society Reagent Grade, having a maximum density of 0.7857 g/mL at 25°C.
NOTE 1—See Annex A1 for the safety and health precautions to be used with acetone.
5.2 Prior to conducting the test, check the density of the acetone with a precision hydrometer to determine its dryness. If the
density of the acetone is gr
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2152 − 17 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
1
Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone Immersion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2152; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* not be used as the only test specification for purchasing of PVC
pipe and fittings. This test only detects inadequate fusion and
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the ad-
does not determine the over-all quality of the PVC pipe or
equacy of fusion of extruded rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)
fittings.
pipe and molded fittings as indicated by reaction to immersion
in anhydrous acetone. 3.2 This test method is useful in determining whether
inadequate fusion contributed to failure of PVC pipe or fittings
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
in other physical or chemical tests, or in service.
as the standard except where instruments are calibrated in SI
units. 3.3 This test method is useful in evaluating the adequacy of
PVC fusion obtained in process or materials trials.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.4 This test method determines adequacy of fusion on a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
single, relatively small specimen. This test method requires the
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
use of a hazardous reagent which must be properly handled and
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to us-
disposed. Therefore, this test method may not be cost-effective
e.Specific hazards statements are given in Annex A1.
to employ as a routine quality control test.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4. Apparatus
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 Container—Either individual, sealable containers for
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
each specimen or one large, airtight container capable of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
holding several specimens without touching one another.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.2 Hydrometer and Cylinder—Precision hydrometer,
graduated in thousandths, with a minimum range of 0.780 to
2. Referenced Documents
0.790 g/mL and a cylinder large enough to immerse the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
hydrometer.
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
4.3 Thermometer—ASTM 12C total immersion
3. Significance and Use thermometer, range from −20°C to 102°C accurate to 0.2°C, or
equivalent.
3.1 This test method is applicable only for distinguishing
between inadequately fused and adequately fused PVC. The
5. Reagent
difference between thermally degraded and adequately fused
5.1 Acetone—American Chemical Society Reagent Grade,
PVC cannot be detected by this test method. Acetone immer-
having a maximum density of 0.7857 g/mL at 25°C.
sion is not a substitute for burst, impact, or other physical or
chemical tests on PVC pipe or fittings and it, therefore, shall
NOTE 1—See Annex A1 for the safety and health precautions to be used
with acetone.
5.2 Prior to conducting the test, check the density of the
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
acetone with a precision hydrometer to determine its dryness.
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl
Based Pipe. If the density of the acetone is greater than 0.934 g/mL at 23°C,
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2017. Published January 2018. Originally
(corresponding to approximately 2 % water by mass (see Fig.
approved in 1963T. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D2152 – 13. DOI:
X1.1)), use fresh acetone or dry the wet acetone with a drying
10.1520/D2152-17.
2
agent. Recheck the density of the fresh or dried acetone before
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
using.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. NOTE 2—Wet acetone can be dried by thoroughly agitating it with at
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2152 − 17
least 15 g of anhydrous calcium sulfate (CaS
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.